import abtem
import ase
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from abtem.finite_difference import DivergedError
from abtem.multislice import MultisliceTransform
abtem.config.set({"device": "cpu"});
abtem.config.set({"local_diagnostics.progress_bar": True});
abtem.config.set({"local_diagnostics.task_level_progress": False});
Multislice using the real space algorithm#
For certain kinds of situations, it is necessary to run the multislice algorithm fully in real space and not rely on Fourier transforms. This will incur a performance penalty, however, so this method is not used by default.
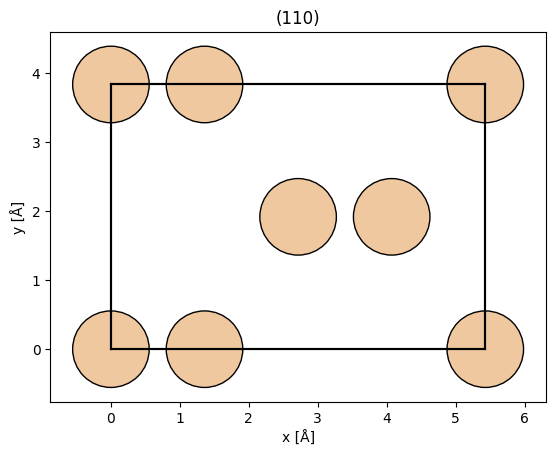
Let’s demonstrate this for Si in the (110) orientation.
desired_rotation = 45
silicon = ase.build.bulk("Si", cubic=False)
# Rotates silicon structure by 45 degrees.
rotated_silicon = silicon.copy()
rotated_silicon.rotate(desired_rotation, "x", rotate_cell=True)
rotated_silicon, transform = abtem.orthogonalize_cell(
rotated_silicon, max_repetitions=10, return_transform=True
)
rotated_silicon.center(axis=2)
abtem.show_atoms(
rotated_silicon, show_periodic=True, scale=0.5, title="(110)", plane="xy"
);
Create a potential.
potential_unit = abtem.Potential(
rotated_silicon,
slice_thickness=0.5,
sampling=0.05,
projection="finite",
)
potential = abtem.CrystalPotential(potential_unit, repetitions=(1, 1, 10))
plane_wave = abtem.PlaneWave(energy=200e3)
plane_wave.grid.match(potential)
Simulations currently requires importing the MultisliceTransform object. You can set the order of the accuracy of the finite difference derivative stencil using the derivative_accuracy keyword. The total number of terms in the series expansion is determined by a convergence criteria.
from abtem.finite_difference import finite_difference_coefficients
transform = MultisliceTransform(potential, method="realspace", derivative_accuracy=8)
exit_wave_rms = plane_wave.build().apply_transform(transform).compute()
transform = MultisliceTransform(potential, method="conventional")
exit_wave_cms = plane_wave.build().apply_transform(transform).compute()
OMP: Info #276: omp_set_nested routine deprecated, please use omp_set_max_active_levels instead.
abtem.stack((exit_wave_rms, exit_wave_cms), ("Realspace", "Conventional")).show(
explode=True, figsize=(12, 4)
);
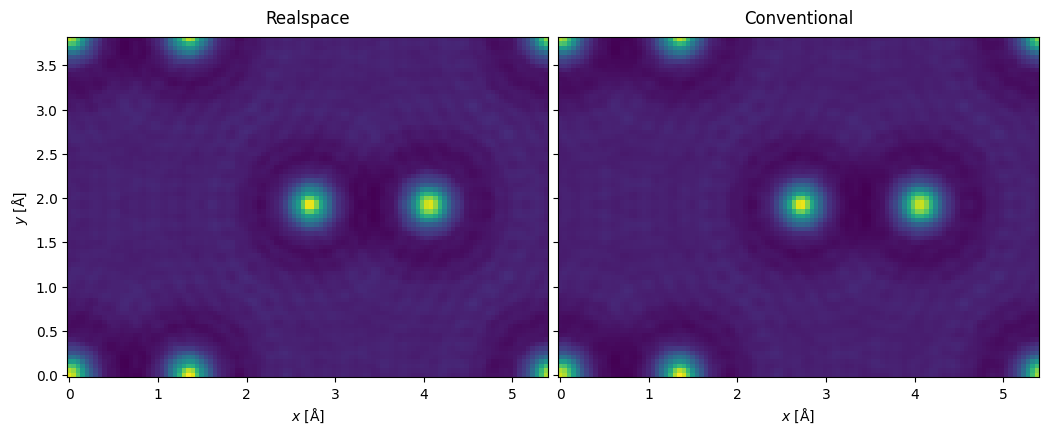
The calculation may diverge if the slices are too thick, you can catch the DivergedError exception. A better sampling also requires a smaller slice thickness.
potential_unit = abtem.Potential(
rotated_silicon,
slice_thickness=2,
sampling=0.05,
projection="finite",
)
potential = abtem.CrystalPotential(potential_unit, repetitions=(1, 1, 10))
plane_wave = abtem.PlaneWave(energy=200e3)
plane_wave.grid.match(potential)
try:
transform = MultisliceTransform(
potential, method="realspace", derivative_accuracy=8
)
exit_wave_rms = plane_wave.build().apply_transform(transform).compute()
except DivergedError:
print("calculation diverged")
calculation diverged
