PRISM quickstart#
This is a short example of running a STEM simulation of a supported nanoparticle with the PRISM algorithm. See our tutorial for a more in depth description.
Configuration#
We start by (optionally) setting our configuration. See documentation for details.
Atomic model#
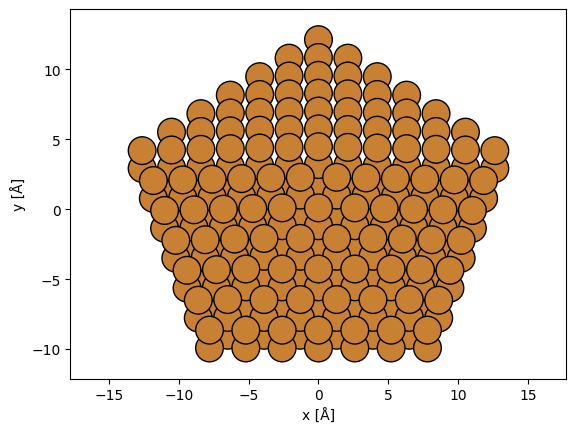
We create an atomic model of a decahedral copper nanoparticle. See our walkthough or our tutorial on atomic models.
cluster = Decahedron("Cu", 7, 2, 0)
cluster.rotate("x", 30)
abtem.show_atoms(cluster, plane="xy");
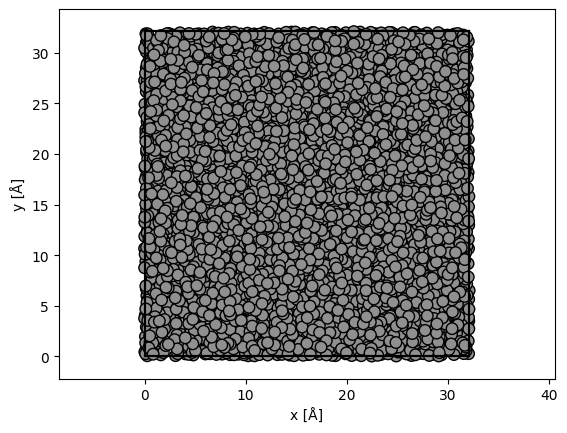
A rough model of amorphous carbon is created by randomly displacing the atoms of a diamond structure
substrate = ase.build.bulk("C", cubic=True)
# repeat diamond structure
substrate = substrate * (9, 9, 20)
# displace atoms with a standard deviation of 50 % of the bond length
bondlength = 1.54 # Bond length
substrate.positions[:] += np.random.randn(len(substrate), 3) * 0.5 * bondlength
# wrap the atoms displaced outside the cell back into the cell
substrate.wrap()
abtem.show_atoms(substrate, plane="xy", merge=0.5);
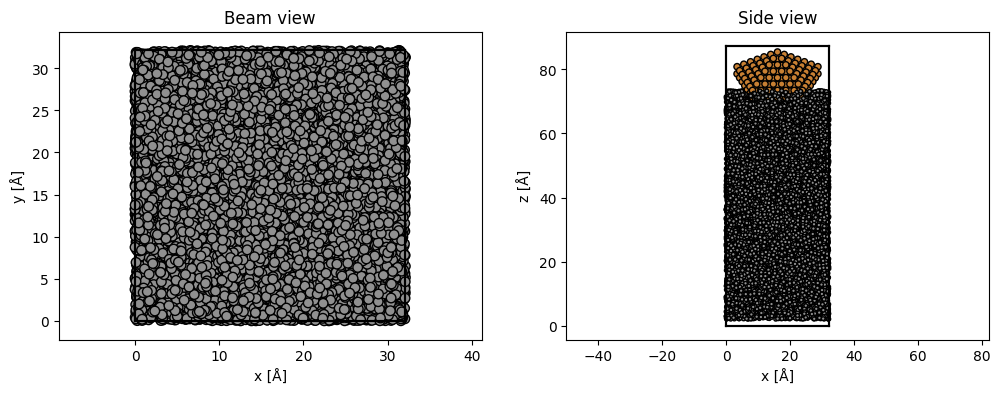
translated_cluster = cluster.copy()
translated_cluster.cell = substrate.cell
translated_cluster.center()
translated_cluster.translate((0, 0, 40))
atoms = substrate + translated_cluster
atoms.center(axis=2, vacuum=2)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
abtem.show_atoms(atoms, plane="xy", ax=ax1, title="Beam view")
abtem.show_atoms(atoms, plane="xz", ax=ax2, title="Side view");
Potential#
We create an ensemble of potentials using the frozen phonon model. See our walkthrough on frozen phonons.
frozen_phonons = abtem.FrozenPhonons(atoms, 8, sigmas=0.1)
We create a potential from the frozen phonons model, see walkthrough on potentials.
potential = abtem.Potential(
frozen_phonons,
gpts=512,
slice_thickness=2,
)
SMatrix#
We create the ensemble of SMatrices by providing our potential, an acceleration voltage \(200 \ \mathrm{keV}\), a cutoff of the plane wave expansion of the probe of \(20 \ \mathrm{mrad}\) and an interpolation factor of 4 in both \(x\) and \(y\). See our tutorial on PRISM for more details.
s_matrix = abtem.SMatrix(
potential=potential,
energy=100e3,
semiangle_cutoff=20,
interpolation=4,
downsample=True,
)
s_matrix.shape
(8, 69, 512, 512)
Contrast transfer function#
To include defocus, spherical aberration and other phase aberrations, we should define a contrast transfer function. Here we create one with a spherical aberration of \(8 \ \mu m\), the defocus is adjusted to the according Scherzer defocus.
Cs = 8e-6 * 1e10 # 8 micrometers
ctf = abtem.CTF(Cs=0, defocus=[0, 80], energy=s_matrix.energy)
We always ensure that the interpolation factor is sufficiently small to avoid self-interaction errors. We can check that by showing the equivalent probe at the entrance and exit plane.
s_matrix.dummy_probes(ctf=ctf).show(explode=True);
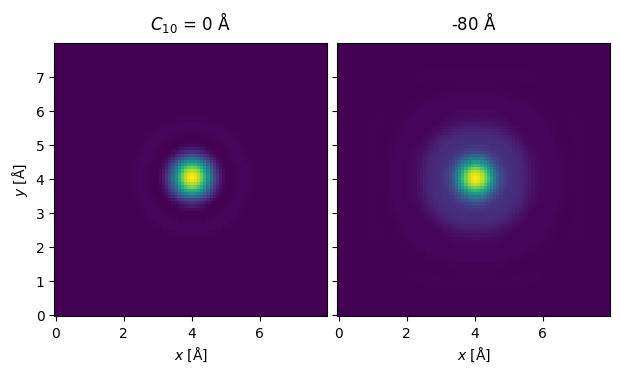
We should also check that our real space sampling is good enough for detecting electrons at our desired detector angles. In this case up to \(\sim 200 \ \mathrm{mrad}\). See our description of sampling.
s_matrix.cutoff_angles
(196.99522495070337, 196.99522495070337)
Create a detector and a scan#
detectors = abtem.FlexibleAnnularDetector()
flexible_measurement = s_matrix.scan(
detectors=detectors, ctf=ctf, reduction_scheme="multiple-rechunk"
)
Depending on the amount of memory available it can be necessary to limit the number of workers.
flexible_measurement.compute(num_workers=8);
<abtem.measurements.PolarMeasurements at 0x1c9113890>
Integrate measurements#
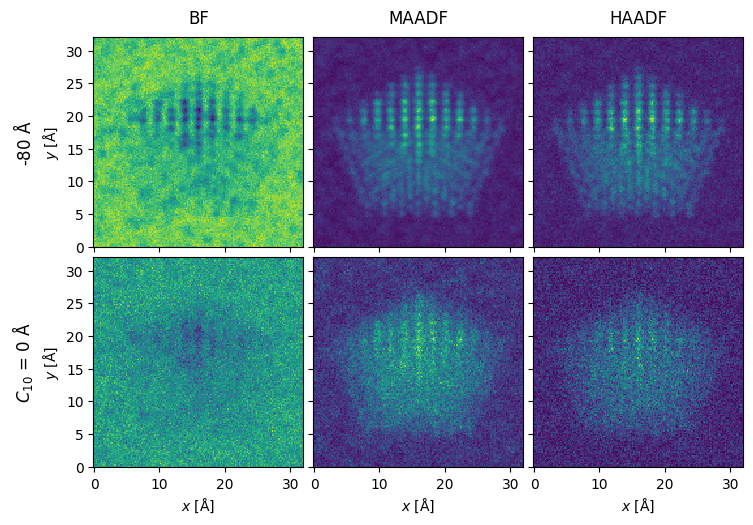
The measurements are integrated to obtain the bright field, medium-angle annular dark field and high-angle annular dark field signals.
bf_measurement = flexible_measurement.integrate_radial(0, s_matrix.semiangle_cutoff)
maadf_measurement = flexible_measurement.integrate_radial(45, 150)
haadf_measurement = flexible_measurement.integrate_radial(70, 190)
measurements = abtem.stack(
[bf_measurement, maadf_measurement, haadf_measurement], ("BF", "MAADF", "HAADF")
)
Postprocessing#
filtered_measurements = measurements.gaussian_filter(0.20).interpolate(0.2)
filtered_measurements.show(
explode=True,
figsize=(14, 5),
);
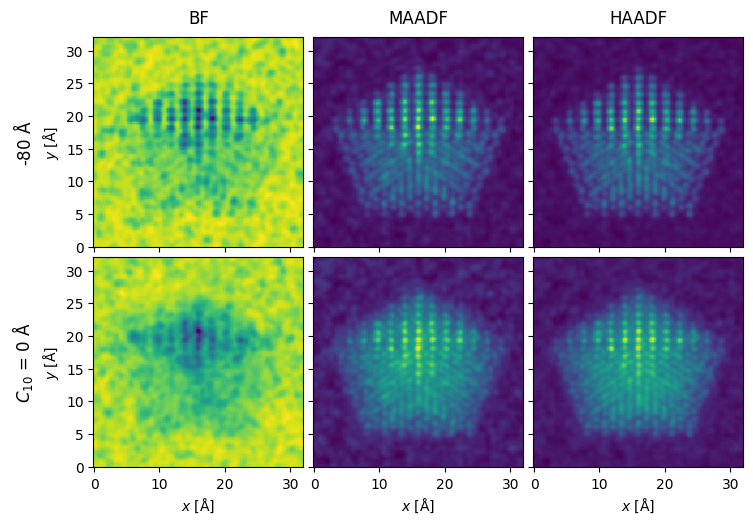
noisy_measurements = filtered_measurements.poisson_noise(dose_per_area=2e4)
noisy_measurements.show(
explode=True,
figsize=(14, 5),
# cbar=True,
);